Featured
Collision Theory Rate Of Reaction
Collision Theory Rate Of Reaction. Although the collision theory of reaction rate is logical, but it has following limitations: The collision theory is based on the assumption that for a reaction to occur it is necessary for the reacting species (atoms or molecules) to come together or collide with one another.
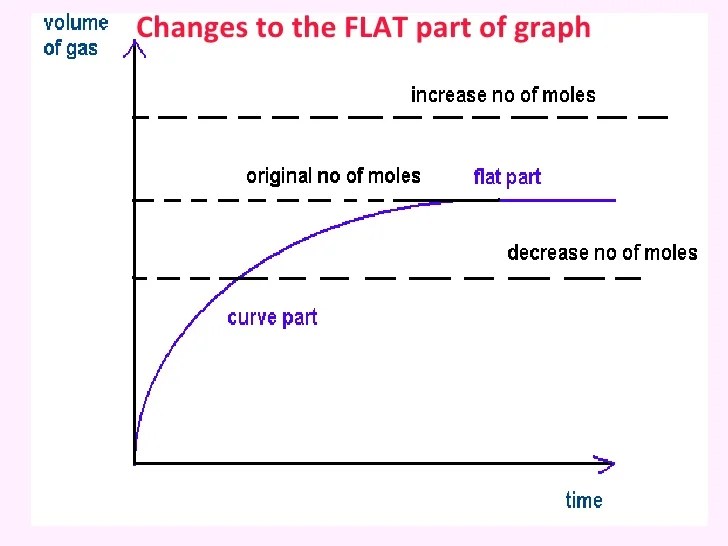
Limitations of collision theory the collision theory of reaction rate is extremely successful in rationalizing the kinetics of many reactions, however, it does suffer from some serious limitations discussed below. As a result, the larger the surface area, the faster. It helps explain how chemical reactions occur.
Rate Of Reaction Can Be Measured In Three Ways.
When a reaction occurs slowly, this means they have a low rate of reaction. It states that successful reactions occur when reactants collide with enough kinetic energy and in the correct orientation to break the bonds and allow the formation of products to occur. Not all collisions, however, bring about chemical change.
Collision Theory States That Chemical Reactions Occur Between Particles When The Molecules Collide Together, If They Have Enough Energy To Cause A Reaction.
Although the collision theory of reaction rate is logical, but it has following limitations: For a chemical reaction to occur, the reactant molecules must collide with enough energy. Collision theory explains the conditions for a chemical reaction to occur between reactants.
According To Which Theory Or Law Is A Chemical Reaction Most Likely To Occur When Two Particles With The Proper Energy And Orientation Interact With Each Other?
Collision theory, theory used to predict the rates of chemical reactions, particularly for gases. It helps explain how chemical reactions occur. How does the collision theory relate to the rate of reaction?
Limitations Of Collision Theory The Collision Theory Of Reaction Rate Is Extremely Successful In Rationalizing The Kinetics Of Many Reactions, However, It Does Suffer From Some Serious Limitations Discussed Below.
In a successful chemical reaction. H 2 o 2 is bit stable at room. Determine the order of the reaction in ki and fecl 3.
Experiment #25 From Advanced Chemistry With Vernier.
But it does tell us the relative rate of consumption of reactants and formation of products. It also helps explain why the rates of reaction are different for different reactions. Within the scope of collision theory, the rate.
Popular Posts
How Does Paleomagnetism Support The Theory Of Plate Tectonics
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment